JERUSALEM — The two-dose Covid-19 vaccine developed by Pfizer and BioNTech is protecting recipients about as well in wide actual use as it did in clinical trials, according to a new large-scale study from Israel that was published on Wednesday in The New England Journal of Medicine.
The study, by the Clalit Research Institute, the research arm of Israel’s largest H.M.O. in collaboration with experts from Harvard University and Boston Children’s Hospital, found that the vaccine reduced symptomatic cases by 94 percent a week after the second dose, and reduced severe disease by 92 percent.
The study appears to be the first large-scale, peer-reviewed examination of the vaccine’s performance in general use. It included more than a million people aged 16 and over, nearly 600,000 of whom had been vaccinated, and an equally large, carefully matched control group of unvaccinated individuals.
The results reflect those of earlier studies out of Israel, as well as clinical trials showing a 95 percent efficacy rate for the vaccine.
“You’re never quite sure, after a controlled trial, will it really look like this in the real world?” Dr. Phil R. Dormitzer, vice president and chief scientific officer of viral vaccines at Pfizer, said in an interview. “So that’s some good news.”
Israel’s swift inoculation campaign has outpaced the rest of the world, making the country a kind of test laboratory for the two-dose Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. More than half the nation’s nine million people have received the first dose, and more than one-third have received both.
The country has universal health care, and about 53 percent of the population is enrolled in Clalit Health Services, giving researchers access to a huge pool of data that could be used to make certain that they were drawing sound conclusions.
“In all studies of vaccine effectiveness, a major challenge is to ensure that those we are comparing to identify the vaccine’s effect are similar in the other characteristics that may predict whether they get infected or ill,” said Prof. Marc Lipsitch of the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, who took part in the study. “Clalit’s extraordinary database made it possible to design a study that addressed these challenges.”
“We have more than 20 years of fully digitized electronic medical records,” said Prof. Ran Balicer, who directs Clalit’s research institute and is the senior author of the new study.
The study included some 22,000 vaccine recipients aged 80 or above, a much larger sample of this exceedingly high-risk category than Pfizer had in its randomized clinical trials. The new study found no drop in effectiveness for the vaccine among older people.
“This research is a perfect example of how randomized trials and observational health care databases complement each other,” Prof. Miguel Hernán, another Harvard researcher who took part in the study, said in a statement.
The study began when Israel started its vaccination drive on Dec. 20, and continued until Feb. 1 — a period when Israel was going through its third and largest wave of infection, and when the B.1.1.7 variant, first detected in Britain, was becoming the dominant source of new cases in Israel. The study indicated that the vaccine is effective against that variant.
Katie Thomas contributed reporting.
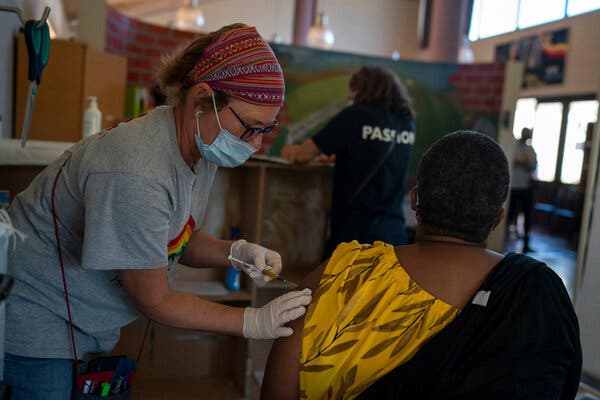

The one-shot coronavirus vaccine made by Johnson & Johnson provides strong protection against severe disease and death from Covid-19, and may reduce the spread of the virus by vaccinated people, according to new analyses posted online by the Food and Drug Administration on Wednesday.
The vaccine had a 72 percent overall efficacy rate in the United States and 64 percent in South Africa, where a highly contagious variant emerged in the fall and is now driving most cases. The efficacy in South Africa was seven percentage points higher than earlier data released by the company.
The vaccine also showed 86 percent efficacy against severe forms of Covid-19 in the United States, and 82 percent against severe disease in South Africa. That means that a vaccinated person has a far lower risk of being hospitalized or dying from Covid-19.
The analyses confirmed that Americans are likely to benefit soon from a third effective coronavirus vaccine developed in under a year, as demand for inoculations greatly outstrips supply. The F.D.A. could authorize the vaccine as early as Saturday, depending on a vote by its vaccine advisory panel on Friday after it discusses the newly released documents.
“With a J&J vaccine, we’ll be able to accelerate the vaccine rollout for our country and for the world,” said Dan Barouch, a virologist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston who led much of the early research on the vaccine last year.
Johnson & Johnson’s vaccine can be stored at normal refrigeration temperatures for at least three months, making its distribution considerably easier than the authorized vaccines made by Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech, which require two doses and must be stored at frigid temperatures.
But access to the new vaccine could be severely limited at first. Dr. Richard Nettles, the vice president of U.S. medical affairs at Janssen Pharmaceuticals, the drug development arm of Johnson & Johnson, told lawmakers on Tuesday that nearly four million doses would be ready for shipment if the F.D.A. authorizes the vaccine, far below the 12 million it had originally pledged to give the federal government by the end of February.
He said that a total of 20 million doses will be ready by the end of March, 17 million fewer doses than the firm’s federal contract envisioned. But he insisted that Johnson & Johnson will fulfill its promise of 100 million doses by the end of June.
Asked about the shortfall on Wednesday, Jeffrey D. Zients, the White House coordinator of the pandemic response, said the Biden administration learned that Johnson & Johnson was behind on manufacturing and needed federal help for equipment and raw materials when it took office in January.
“It was disappointing when we arrived” he said, but “I think the progress is real.” Despite the delays, he said, “obviously the prospect of a potential third approved vaccine is very encouraging” because lack of supply remains the biggest obstacle to the nation’s vaccination effort.
Mr. Zients said if the new vaccine is authorized, roughly two million of the initial four million or so doses would be added to the shipments from Moderna and Pfizer to the United States next week. The remainder would go to federal vaccination programs at pharmacies and community health centers, he said.
Johnson & Johnson’s vaccine has a lower efficacy rate than the vaccines from Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech, which are both around 95 percent.
But in South Africa, the Johnson & Johnson vaccine is so far the clear winner. Novavax’s shot had an efficacy of 49 percent in South Africa. And a small trial in South Africa of the AstraZeneca-Oxford vaccine found that it did not offer much protection at all. The negative results led the South African government to abandon its plan of giving a million doses of AstraZeneca vaccines to health care workers. Last week, the government started giving Johnson & Johnson’s vaccines instead, and has so far administered more than 32,000.
The newly released documents, which include the F.D.A.’s first technical analysis of the company’s 45,000-person clinical trial, presented evidence that the vaccine was safe, with noticeably milder side effects than the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines and without any reports of severe allergic reactions like anaphylaxis.
The vaccine’s protection was consistent across Black, Hispanic and white volunteers, and also across different ages. The trial indicated a lower efficacy, of 42.3 percent, for people over 60 who had risk factors like heart disease or diabetes. But this figure came with a large amount of statistical uncertainty, the F.D.A. noted.
Although several vaccines can protect people from getting sick with Covid-19, it is unclear whether the shots can also prevent people from getting infected and passing the virus to others, leading to a debate about how quickly society can return to normal after inoculations begin.
Moderna’s trial found some hints that vaccinated people were less likely to develop an infection without symptoms. And AstraZeneca found that its vaccine reduced asymptomatic infections by about half.
Johnson & Johnson looked for asymptomatic infections by checking for coronavirus antibodies 71 days after volunteers got a vaccine or a placebo. The new analyses estimate that the vaccine has an efficacy rate of 74 percent against asymptomatic infections. But that calculation was based on a relatively small number of volunteers, and the F.D.A. noted that “There is uncertainty about the interpretation of these data and definitive conclusions cannot be drawn at this time.”
“I think it’s going to add to the growing evidence that the vaccines really do prevent infection as well as prevent disease,” Dr. Barouch said.
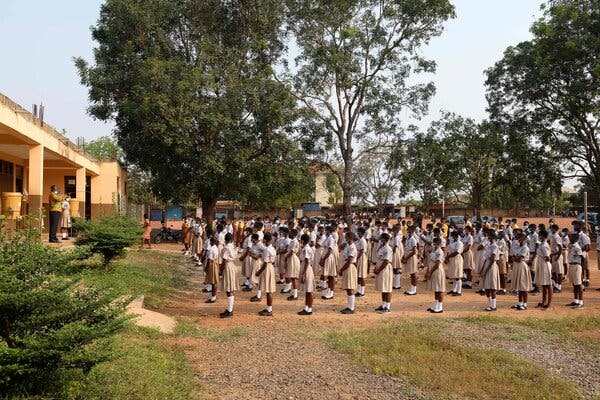

The global sharing program designed to make vaccine access more equal delivered its first major shipment of doses on Wednesday to the West African nation of Ghana, ramping up the largest mass immunization campaign in history.
“Today marks the historic moment for which we have been planning and working so hard,” said Henrietta Fore, the executive director of UNICEF. “In the days ahead, frontline workers will begin to receive vaccines, and the next phase in the fight against this disease can begin.”
The first shipment of 600,000 doses was packed up and labeled in India, then flown to Accra, the Ghanaian capital.
Ghana and other West African countries are to begin vaccinations in coming days, according to officials, the first of 92 low and middle-income countries that will receive free vaccines through Covax, a vaccine-sharing initiative.
The goal is for Covax to deliver some two billion doses of Covid-19 shots this year, which officials said would make it the largest vaccine procurement and supply operation in history.
The shipment arrived in West Africa as studies were released suggesting that the spread of the virus in the region has been much wider than official numbers show.
At least one in five people in Lagos, Nigeria, could have had contracted the coronavirus by October last year, according to findings just released by the Nigeria Center for Disease Control, an infection rate far higher than the one reported through the national surveillance system. A study in Accra released in November had similar findings.
Many public health officials have criticized the unequal distribution of vaccines — with wealthy nations already delivering tens of millions of doses and acquiring vast reserves for their populations.
For instance, while at least 44.5 million Americans and around 18 million people in Britain have already received a shot, as of last week more than 130 countries had yet to vaccinate a single person. The Ghana shipment covers just 1 percent of the population.
The United Nations secretary-general, António Guterres, said last week that the distributions had been “wildly uneven and unfair.”
And high-income countries are not respecting contracts under Covax and are competing with them, reducing the number of doses the initiative can buy, Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, the head of the World Health Organization, said on Tuesday.
The pandemic will not end, he added, until everyone is vaccinated.
“This is not a matter of charity,” he said. “It’s a matter of epidemiology.”
Last week, the group of wealthy industrialized nations known as the Group of 7 announced that they would intensify their cooperation with the international vaccination drive and raised their overall commitment to the effort to $7.5 billion.
But Dr. Tedros said that there remained a financing gap of $23 billion.
President Emmanuel Macron of France called for even more urgent action on Friday, saying Europe and the United States should send up to 5 percent of their vaccine supplies to developing nations.
But even if things go according to plan, vaccinating the vast majority of the world’s most vulnerable people this year will be a daunting challenge.
Ghana, a nation of more than 30 million people, will get enough vaccines to cover only about 20 percent of its population by the end of 2021. It will have to buy millions more doses separately.
Poorer countries do not pay to purchase vaccines and injection devices under Covax, at least for up to 20 percent of the population. But they do have to pay the costs of delivery within the country.
To receive vaccines, countries had to submit plans saying who they wanted to immunize, how they would go about it and how they would monitor vaccinations. They also had to sign an indemnity agreement with the vaccine manufacturer.
“No country was prioritized,” said Benjamin Schreiber, UNICEF’s coordinator for the Covax program.
Four countries eligible to apply for vaccines under Covax did not do so: Burundi, Eritrea, Madagascar and Tanzania.

A meta-analysis of studies released on Wednesday affirmed what social workers, educators and law enforcement officials have warned about for months: Stay-at-home orders exacerbated domestic violence. Reports increased more than 8 percent since the widespread lockdowns in the United States began last spring.
The report, released by a University of Miami sociology professor, Alex R. Piquero, and the National Commission on Covid-19 and Criminal Justice, is based on 18 studies covering communities in the United States and overseas. It compared changes in the number of domestic violence events before and after lockdowns began.
The studies measured changes in police calls for service, crime and incident reports, domestic violence hotline registries, and health records, using data derived from official records. The studies did not use qualitative or anecdotal evidence.
“We were able to quantify, in large and small U.S. cities and some worldwide, a broad view of the impact that the pandemic has had on domestic violence,” Mr. Piquero, the lead author of the report, said in an interview.
Even before this study, with only limited data available, the situation was deemed so grave that the World Health Organization and the United Nations called for action to protect children from violence amid lockdowns.
When the researchers factored in data from a few countries outside the United States — including Argentina, Italy, Mexico and Sweden — they found that the rate of domestic violence was only slightly lower.
Given that domestic violence is one of the most underreported crimes, Mr. Piquero said that the report’s findings were most likely an underestimate.
“This is a floor, not a ceiling, with regard to the true veracity of what the pandemic did to domestic violence,” he said.
The report reiterated what was already evident in anecdotal accounts of domestic violence during the pandemic: The lockdowns forced adults and children to stay in close quarters with their abusers, and the orders cut them off from friends, neighbors, colleagues and others who could report signs of abuse or help victims escape violent situations.
The economic impact of the pandemic also exacerbated factors already associated with domestic violence, including male unemployment, financial insecurity, and alcohol and other substance use, according to the study.
The group that compiled the study, the National Commission on Covid-19, was created by the Council on Criminal Justice, a think tank that studies criminal justice policies. It is led by a bipartisan pair of former attorneys general: Alberto Gonzales, a Republican, and Loretta Lynch, a Democrat.
The commission aims to assess the pandemic’s impact on the justice system; it includes judges, law enforcement officials, a defense lawyer, a researcher, and community and religious leaders.
The commission said that its findings highlighted a serious need for more domestic abuse prevention and services for survivors. It said the need was especially urgent among historically marginalized groups and those likely to be disproportionately isolated during the pandemic, such as older adults, people struggling with mental illness and chronic health conditions, and women and children with past experiences of violence and abuse.

The Biden administration plans to send more than 25 million masks to food banks and community health centers in low-income neighborhoods across the country next month as part of its push to deliver equitable care during the pandemic and “level the playing field,” Jeffrey D. Zients, the White House coronavirus response coordinator, said on Wednesday.
“Not all Americans are wearing masks regularly. Not all Americans have access, and not all masks are equal,” Mr. Zients said during a news briefing. The masks, he said, will be made in the United States in compliance with guidance from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. They will also be reusable, available in adult and child sizes, and free at 60,000 food banks and 1,300 community centers in areas that have suffered deeply during the pandemic.
The initiative, which costs $86 million, combines two of President Biden’s top efforts to fight the pandemic: His call for all Americans to wear masks, mandating face coverings on federal property; and his pledge to ensure that underserved communities have what they need to protect themselves from the virus.
Researchers have found that the pandemic has affected Black and Hispanic people in the United States disproportionately compared with white people because of social and environmental factors.
Mr. Zients said federal health officials are routinely looking at data to identify the populations most in need. Collecting accurate data on the race and ethnicity of people being vaccinated against the coronavirus has been challenging for federal officials, hampering Mr. Biden’s push for racial equity.

A large nationwide study has found important differences between the two major ways children have become seriously ill from the coronavirus. The findings may help doctors and parents better recognize the disease and understand more about the children who are at risk for either condition.
The study, published Wednesday in JAMA, analyzed 1,116 cases of young people who were treated at 66 hospitals in 31 states between March 15 and Oct. 31, 2020. About half the patients in the study had acute Covid-19, the predominantly lung-related illness that afflicts most adults who get sick. The rest had the inflammatory syndrome that has emerged in some children weeks after an initial infection that typically was mild.
The researchers found some similarities, but also significant differences, in the symptoms the two groups experienced and in the characteristics of the patients, who ranged in age from infants to 20-year-olds.
Young people with the syndrome, called Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children or MIS-C, were more likely to be between 6 and 12; more than 80 percent of the patients with acute Covid-19 were either younger than 6 or older than 12.
More than two-thirds of patients with either condition were Black or Hispanic, which experts say probably reflects the fact that those groups have been exposed disproportionately to the virus for socioeconomic and other reasons. But while Hispanic young people seemed to be at equal risk of developing either condition, Black children appeared to be at greater risk for developing the inflammatory syndrome than the acute illness, according to Dr. Adrienne Randolph, a pediatric critical care specialist at Boston Children’s Hospital and the senior author of the study.
“That MIS-C kids tended to be between 6 and 12 and Black either speaks to who’s getting infected more broadly, or maybe some true phenomenon about which age and ethnicity is most susceptible to MIS-C or protected from severe acute Covid,” said Dr. Srinivas Murthy, an associate professor of pediatrics at the University of British Columbia, who was not involved in the study.
The researchers found that young people with the inflammatory syndrome were much more likely to have been previously healthy than those with acute Covid were. Still, more than one-third of patients with acute Covid had no previous underlying condition. “It’s not like previously healthy kids are completely scot-free here,” Dr. Randolph said.
Young people with the inflammatory syndrome were more likely to need treatment in an intensive care unit, and their symptoms were much more likely to include heart problems and inflammation and to involve the skin and mucous membranes, than the patients with acute Covid were. But roughly the same proportions of patients with each condition needed respiratory support, including ventilators, and roughly the same small number of patients in each group died — 10 young people with MIS-C, and eight with acute Covid.

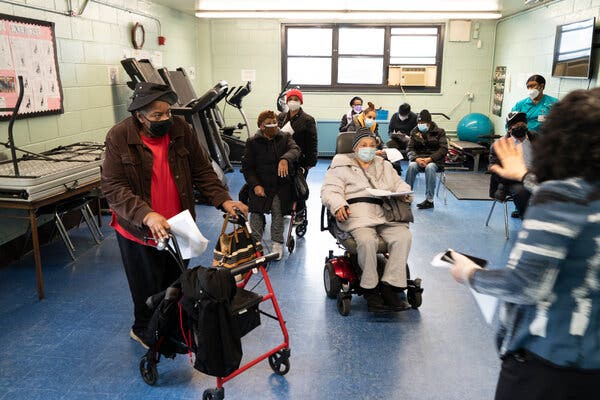
New York State opened two large vaccination sites on Wednesday in Brooklyn and Queens, part of an effort to boost inoculations in neighborhoods that have been hit particularly hard by the pandemic and where residents include some of those most vulnerable to severe illness from the virus.
The sites, established in partnership with the Federal Emergency Management Agency, were built to “bring the vaccine to the community that needs it most,” said Gov. Andrew M. Cuomo at a news conference at the Queens site, located at York College in Jamaica, on Wednesday. “And we’re going to give that community priority to get the vaccine.”
Each site is expected to provide 3,000 vaccine doses a day; Mr. Cuomo said they are the largest vaccination sites in the state so far.
Appointments are reserved only for eligible people who live in ZIP codes surrounding each location, many of which are home to low-income communities of color and immigrant communities who remain the hardest hit by the virus. After Saturday, the sites will be open to those in the surrounding borough.
At the York College site, the targeted ZIP codes are all in southeastern Queens. They include parts of Jamaica, South Jamaica and Far Rockaway, which were hit particularly hard by the virus and where only 3 or 4 percent of adults have received at least one vaccine dose.
The site in Brooklyn, at Medgar Evers College, will first focus on vaccinating residents in parts of East New York, Brownsville, Bushwick, East Flatbush, Canarsie and Bedford-Stuyvesant, which include some of the poorest neighborhoods in the city and have disproportionately low vaccination rates. It is also open to residents of neighborhoods that have been hit somewhat less severely by the virus, including Crown Heights, Prospect-Lefferts Gardens, Prospect Heights and Clinton Hill, which have large communities of color.
Data released by New York City officials showed that many of the areas being targeted by the state sites had some of the lowest vaccination rates in the city, in some cases lagging significantly behind the share of residents vaccinated in wealthier ZIP codes in Manhattan that have higher proportions of white residents.
Experts say people across the country who live in underserved neighborhoods face a variety of obstacles in getting the vaccine, including registration systems and websites that can take hours to navigate; a lack of transportation; and difficulty getting time off from work to get a shot. Many people in communities of color also are more likely to be hesitant about getting vaccinated, in light of the history of unethical medical research in the United States.
According to the city’s data, white New Yorkers have so far received a disproportionate share of the doses administered. Of city residents who received at least one dose, about 42 percent were white, 15 percent were Latino, 16 percent were Asian and 12 percent were Black. Latino and Black residents were underrepresented: The city’s population is roughly 29 percent Latino and 24 percent Black.
Those eligible to receive the vaccine at the Brooklyn and Queens sites can schedule appointments online, by calling 1-833-697-4829 or by visiting the locations in person between 8 a.m. and 8 p.m. Appointments are required.
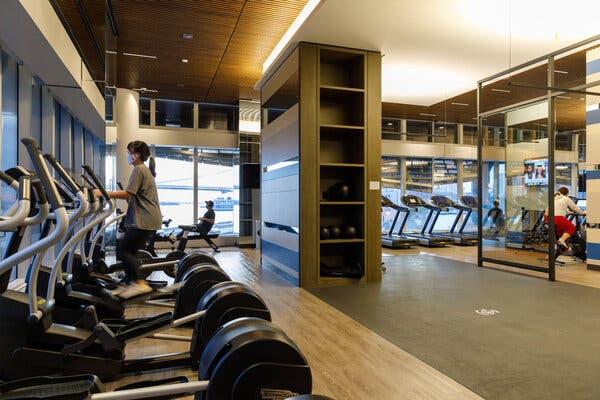

Public health officials on Wednesday urged gym-goers to wear masks when they exercise and to remain six feet apart from others, as new research described the rapid spread of coronavirus infections during high-intensity exercise classes at gyms in Honolulu and Chicago.
Researchers at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention advised fitness facilities to implement a number of measures to prevent outbreaks, including enforcing proper mask use and reminding members and staff to stay home if they have symptoms of illness or have tested positive for the coronavirus.
Heavy breathing during intense physical activity in confined, indoor spaces enhances transmission, and fitness teachers who shouted exercise instructions to members may also have contributed to the spread, the C.D.C. research found. Mask regulation varies by state. Exercising outdoors or taking virtual fitness classes could help reduce infection risk, the authors noted.
“It’s very important for individuals who would like to attend a gym and work out to be cognizant of what the Covid symptoms are, and to be aware that if you are feeling something that looks and feels like a Covid-19 symptom, to stay home as a precaution,” said Richard A. Teran, a C.D.C. epidemiologist in Chicago who was one of the authors of the Chicago case study published on Wednesday.
At a gym in Chicago, Dr. Teran and his colleagues identified 55 coronavirus infections among 81 people who attended high-intensity in-person fitness classes between Aug. 24 and Sept 1.
Among them were 22 people who had gone to the classes on the day or day after they developed their first symptoms of illness. Three went to an exercise class on the same day or day after receiving a positive test result indicating they were infected. In all, 43 gym members who tested positive participated in classes when they were possibly infectious, researchers said.
The outbreak occurred even though classes at the gym were limited to 25 percent of their usual size, with only 10 to 15 people in attendance.
Members were required to wear a mask when they entered the gym, at which point they had their temperatures taken and were screened for symptoms. But they were allowed to remove their masks while exercising; those who were infected were more likely to wear masks infrequently during classes, the researchers found.
In Hawaii, public health investigators linked 21 infections to a 37-year-old male fitness instructor in Honolulu who taught at several facilities and developed symptoms of Covid-19 — body aches, chills, headache and cough — at the end of June, according to a C.D.C. report published on Wednesday.
On June 29, just hours before his first symptoms, he taught an hourlong stationary cycling class with 10 participants, in which no one wore masks. All of those participants tested positive in early July, among them another fitness instructor, a 46-year-old man, who worked at another facility. He became acutely ill and was hospitalized in an intensive care unit.
Twelve hours before the second instructor experienced his first symptoms, he held several small kickboxing sessions and a personal training session. Of 11 people exposed, 10 were infected and tested positive in early July. All 10 developed symptoms, and one was hospitalized in the intensive care unit.
On July 22, the city of Honolulu passed emergency orders requiring face coverings in fitness facilities, including during exercise. Before then, gym members could remove the face coverings while exercising.

For teenagers and young adults who are anxious by nature or feeling emotionally fragile, the pandemic and its social isolation have pushed them to the brink.
Rates of suicidal thinking and behavior are up 25 percent or more from similar periods in 2019, according to an analysis of surveys of young patients in emergency rooms.
For the young people coming undone, pandemic life presents unusual challenges, pediatricians say. Most are temperamentally sensitive and after months of being socially cut off from friends and activities, they have much less control over their moods.
“What parents and children are consistently reporting is an increase in all symptoms — a child who was a little anxious before the pandemic became very anxious over this past year,” said Dr. Adiaha I. A. Spinks-Franklin, an associate professor of pediatrics at the Baylor College of Medicine. It is this prolonged stress, Dr. Spinks-Franklin said, that in time blunts the brain’s ability to manage emotions.
For teenagers in a mental health crisis, there aren’t many places to turn. They need help, but it is hard to come up with a psychiatric diagnosis. They are trying to manage a surprise interruption in their lives, a vague loss. And without a diagnosis, reimbursement for therapy is hard to come by. And that is assuming parents know what kind of help is appropriate, and where to find it.
When a crisis does hit, many of these teenagers end up in the local emergency department — the one place desperate families so often go to for help.
Many E.R. departments across the country are now seeing a surge in such cases. Through most of 2020, the proportion of pediatric emergency admissions for mental problems, like panic and anxiety, was up by 24 percent for young children and 31 percent for adolescents compared to the previous year, according to a recent report by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The local emergency department is frequently unprepared for the added burden. Workers often are not specially trained to manage behavioral problems, and families don’t have many options for where to go next, leaving many of these pandemic-insecure adolescents in limbo at the E.R.
“This is a national crisis we’re facing,” Dr. Rebecca Baum, a developmental pediatrician in Asheville, N.C. “Kids are having to board in the E.R. for days on end, because there are no psychiatric beds available in their entire state, never mind the hospital. And of course, the child or adolescent is lying there and doesn’t understand what’s happening in the E.R., why they’re having to wait there or where they’re going.”

If you’re lucky enough to have traveled by air to, say, Kauai or the British Virgin Islands, your quarantine may include the option of roaming relatively freely on a resort’s expansive grounds while waiting for a negative coronavirus test.
But travel by air to Australia, New Zealand, mainland China or Tunisia, and you will generally find yourself confined to your room, 24 hours a day, for up to two weeks (assuming you test negative, that is). And with some exceptions, you are footing the bill — quarantine in New South Wales, Australia, for example, costs 3,000 Australian dollars, or about $2,300, for a two-week quarantine for one adult, and up to 5,000 dollars for a family of four.
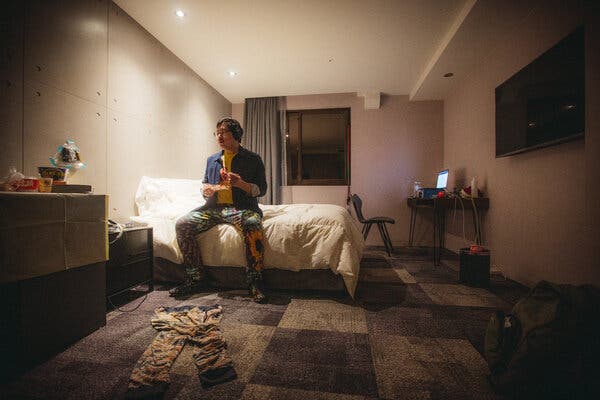
Quarantine might seem manageable for those who have been living under shelter-in-place orders and working from home. Pete Lee, a filmmaker based in San Francisco, was not concerned about the quarantine when he flew to Taiwan for work and to visit family.
“I was a little bit cocky when I first heard about the requirement,” Mr. Lee said, during his eighth day at the Roaders Hotel in Taipei, Taiwan. “I was inside my San Francisco apartment for 22 out of 24 hours a day! But it’s a surprisingly intense experience. Those two hours make a big difference.”
Joy Jones, a coach and educator who is based in San Francisco, traveled to New Zealand with her husband, a New Zealand citizen, and two young daughters in January. She learned before their departure that they would have no say where they would be quarantined.
“That was probably the hardest part,” she said. “I could put together a bag of activities for my older daughter, and plan on doing laundry in the sink. But not having an answer to where we’d be — after more than 21 hours of flying, with masks — would we have to get another flight? A three-hour bus ride?” They didn’t. Ms. Jones and her family were taken to Stamford Plaza in Auckland, just 25 minutes from the airport.
The challenge is managing the tedium.
“We decorated a paper horse that we hung in our window — every day, a different part of it — that was a favorite activity. We’d have dance parties. And we’d watch a movie every night. We did what we could to bring some fun into it,” Ms. Jones said.
She documented her family’s quarantine experience on her private Instagram account, showing forts made of blankets, paper airplane competitions and “bowling” with water bottles and a crumpled ball made of paper. She was touched that friends and family sent her family meals, treats and toys in response to her posts.
“It was a really cool way to feel love, and connection, from such an isolated space,” she said.

The coronavirus pandemic has crippled economies, shut down travel and claimed hundreds of thousands of lives, transforming the world in ways that would have been unthinkable a year ago. The Biden administration’s first days were inevitably dominated by discussion of how his team would tackle the crisis, as the U.S. death toll continued its inexorable climb to a staggering milestone: 500,000 deaths.
Here’s a look at the key figures on President Biden’s Covid-19 response team, and some of their plans to try to stop the spread of the virus and regain some semblance of normalcy.
Dr. Anthony S. Fauci
Chief medical adviser.
The longtime head of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, Dr. Fauci said he accepted the president’s offer to be his chief medical adviser “right on the spot.” Considered the nation’s leading infectious disease expert, he has been an adviser to every president since Ronald Reagan, and was awarded the Presidential Medal of Freedom by George W. Bush for his work fighting H.I.V./AIDS. But he became a household name only after the start of the pandemic, when he emerged as a trusted authority in countless news briefings, interviews and public appearances.
Dr. Rochelle P. Walensky
Director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Dr. Walensky, previously chief of the division of infectious diseases at Massachusetts General Hospital and a professor at Harvard Medical School, replaced Dr. Robert R. Redfield. She has also focused on H.I.V./AIDS in her career, and has served as chair of the Office of AIDS Research Advisory Council at the National Institutes of Health, and as an adviser to the World Health Organization. Dr. Walensky has pledged to restore public trust in the agency and to provide accurate information “even when the news is bleak, or when the information may not be what those in the administration want to hear.”
Xavier Becerra
Nominee for secretary of health and human services.
Mr. Becerra was appointed as attorney general of California in 2017, when his predecessor, Kamala Harris, joined the Senate, and he was elected to a full term in 2018. He became known as a lead attacker in the Trump resistance, filing roughly 100 lawsuits against the administration on issues including climate change, gun control and health care. Notably, he led 20 states and the District of Columbia in a campaign to protect the Affordable Care Act. Before serving as attorney general, he spent 24 years in Congress, representing a Los Angeles district. If confirmed, he would be the first Latino to run the mammoth department, which has a budget of more than $1 trillion. He pledged at a Senate confirmation hearing on Tuesday to find “common cause” with his critics, and is scheduled to appear on Wednesday before the Senate Finance Committee.
Dr. Vivek H. Murthy
Nominee for surgeon general.
Dr. Murthy served as surgeon general under President Barack Obama — he was one of the youngest ever — and is Mr. Biden’s nominee for the same position. He is a physician who has taught at Harvard Medical School and served as vice admiral of the U.S. Public Health Service Commissioned Corps. Dr. Murthy has been outspoken about linking public health and wellness. His book “Together: The Healing Power of Human Connection in a Sometimes Lonely World” was published last year. His confirmation hearing is scheduled to begin Thursday.
Dr. Marcella Nunez-Smith
Chair of the Covid-19 Health Equity Task Force.
A physician and public health specialist at Yale University, Dr. Nunez-Smith is leading a team of 12 experts advising the president on how to address the disproportionate impact of Covid-19 on vulnerable communities. Dr. Nunez-Smith grew up in the U.S. Virgin Islands and came from a family of health care providers. She has spoken in interviews about how seeing her father suffer a debilitating stroke in his 40s, caused by untreated high blood pressure, spurred her to work in public health.
Jeffrey D. Zients
Coordinator of the administration’s Covid-19 response.
Mr. Zients, an entrepreneur and consultant, joined the Obama White House in 2009 and became known as a Mr. Fix-It with strong operational skills. He was tapped to untangle the messy rollout of the Affordable Care Act’s online insurance marketplace in 2013. After Mr. Obama left office, Mr. Zients joined the private equity fund Cranemere as chief executive and also served on Facebook’s board.
Andy Slavitt
Senior White House pandemic adviser.
Mr. Slavitt, a former health care company executive, served as the acting administrator of the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services from 2015 to 2017. (His company was also involved in fixing the A.C.A. website before that.) Mr. Slavitt was outspoken in his defense of the Affordable Care Act during the Trump administration — and raised the alarm about the pandemic early in 2020. He’s active on Twitter, writes on Medium, and until recently, hosted a podcast about Covid. He has said that he accepted the White House job “on a short-term basis.”
Dr. David Kessler
Chief science officer for the Covid-19 response.
Dr. Kessler, a pediatrician and lawyer who was head of the Food and Drug Administration during the presidencies of George Bush and Bill Clinton, will oversee the vaccine program. He will share responsibilities with Gen. Gustave F. Perna, who was the chief operating officer for Operation Warp Speed, the Trump administration’s program to accelerate vaccines and treatments. (The Biden administration later dropped that name.) As F.D.A. commissioner, Dr. Kessler was known for battling the tobacco industry and developing nutrition fact labels on food products. Dr. Kessler is close to Dr. Fauci; the two worked together to speed the development and approval of drugs that changed the course of the AIDS epidemic in the 1990s.
Dr. Janet Woodcock
Acting commissioner of the Food and Drug Administration.
Dr. Woodcock was the longtime head of the F.D.A.’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Review, and worked on Operation Warp Speed. The Biden administration has not yet nominated a permanent commissioner; Dr. Woodcock and Dr. Joshua Sharfstein, a former high-ranking F.D.A. official, are the apparent front-runners.
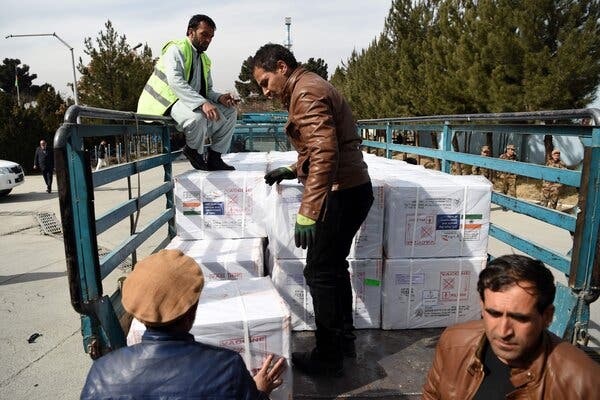

Afghanistan, whose citizens have largely brushed aside the coronavirus pandemic as exaggerated or an outright hoax, is now preparing to distribute its first batch of vaccines.
A half-million doses of the AstraZeneca-Oxford vaccine, produced by an Indian manufacturer, were delivered to the capital, Kabul, on Feb. 7. But the arrival was greeted with indifference by many Afghans, who have rebuffed government warnings that the virus is a deadly public health threat.
The cheap and easy-to-store AstraZeneca-Oxford vaccine is being delivered as part of the Covax program, a worldwide initiative to buy and distribute vaccines to poor countries free or at a reduced cost. On Feb. 15, the World Health Organization authorized use of the vaccine, which requires two doses per person, clearing the path for Afghanistan to begin its inoculation campaign.
Global trials have found that the vaccine offered complete protection against severe disease and death. But its efficacy against the virus variant first identified in South Africa is in question, after the shot failed in a small trial to prevent study participants from getting mild or moderate illness.
The vaccine arrives as Afghanistan is fighting off a second deadly wave, even as most Afghans go about their daily lives as if the virus never existed. Many people refuse to wear masks and cluster in dense crowds inside bazaars, supermarkets, restaurants and mosques, oblivious to ubiquitous public health posters.
In an impoverished nation battered by war, hunger, poverty and drought, an invisible virus is considered fake — or an afterthought.
“Of course I won’t take the vaccine, because I don’t believe in the existence of the coronavirus,” said Muhibullah Armani, 30, a taxi driver in the southern city of Kandahar.
Expressing a sentiment shared by many Afghans, Mr. Armani added, “When I see people covering their mouth and nose, afraid of Covid, it makes me laugh at them.”
global roundup
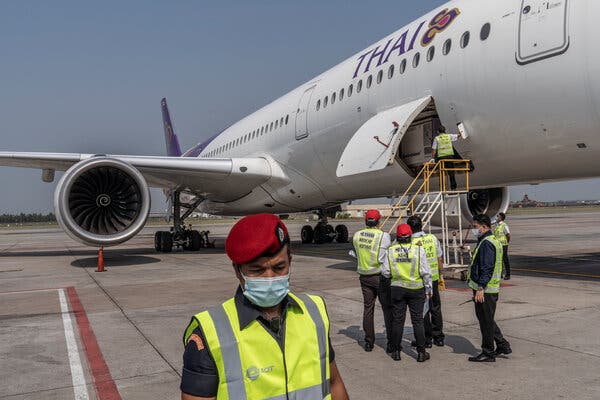

Thailand, which has lagged behind some of its Southeast Asian neighbors in obtaining coronavirus vaccines, received its first shipment Wednesday: 200,000 doses of the CoronaVac shot from China.
Prime Minister Prayuth Chan-ocha and most of his cabinet were on hand at Suvarnabhumi International Airport outside Bangkok to greet the arrival of a Thai Airways cargo plane delivering the doses. The CoronaVac shot was developed by a private Chinese company, Sinovac Biotech, and has faced scrutiny over a lack of data from late-stage clinical trials.
The Thai officials stood in front of a banner proclaiming: “Covid-19 Vaccine: Returning Smiles to Thailand.” The country has long promoted itself as a tourist destination with the slogan “The Land of Smiles.”
Thailand’s Food and Drug Administration approved Sinovac’s vaccine for emergency use on Tuesday. Sinovac is expected to send two million doses in total, with health workers receiving the first inoculations.
So far, only a few governments in Asia have approved CoronaVac for use. Several more have said they would only do so after receiving full trial data from the manufacturer.
In a statement before the CoronaVac shipment arrived, Mr. Prayuth said that 65 million doses of vaccines were planned so far, and that vaccines from other manufacturers would arrive soon. Thailand approved the AstraZeneca vaccine in late January.
Vietnam, which has also been relatively successful in containing the virus but slow to obtain vaccines, received its first shipment Wednesday: 117,000 doses of the AstraZeneca-Oxford vaccine.
Thailand has been among the most successful countries in containing the virus, with fewer than 26,000 cases and 83 deaths since the start of the pandemic. More than 80 percent of the cases have been recorded since December, when the country experienced its most serious outbreak at a seafood market in Samut Sakhon Province. Since then, the number of new cases has fallen to below 100 a day and the government has been gradually easing restrictions.
Thailand’s vaccination plan has been less ambitious than its program of contact tracing and containment. The government has called for inoculating half the country of roughly 70 million people by the end of the year.
In contrast to Thailand’s slow start, Singapore began vaccinations in late December, Indonesia started six weeks ago, and Myanmar nearly a month ago, although its program has been disrupted by the Feb. 1 military coup.
Thailand’s tourism sector, which accounts for about 20 percent of the economy, has pushed for a more aggressive vaccination program to help reopen the country to foreign visitors.
Since the beginning of the outbreak, Thailand has required nearly everyone arriving from overseas to undergo quarantine for 14 days. Mr. Prayuth said on Wednesday that the government was considering whether to allow foreigners who have been vaccinated to skip quarantine.
In other international news:
-
Taiwan said on Wednesday that it would resume allowing short-term business travelers from certain “low-risk” countries to apply to isolate for less than the usual two weeks upon arrival — an exemption that it canceled two months ago amid concerns about the pandemic’s severity. The self-governing island is still closed to tourists and most other nonresidents.
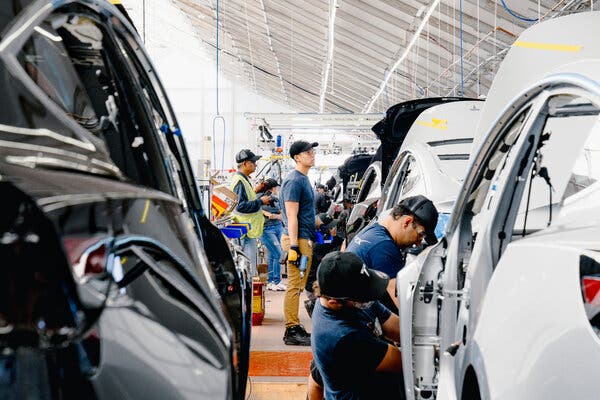

President Biden signed an executive order on Wednesday that will kick off a review of the supply chains that support several crucial American manufacturing industries, including automobiles, pharmaceuticals and clean energy.
The president cast the move as an important step to create good-paying jobs and make the economy more resilient in the face of geopolitical threats, pandemics and climate change. “This is about making sure the United States can meet every challenge we face in the new era,” Mr. Biden said.
The order will not target imports from any specific country, senior Biden administration officials said Tuesday, but it is widely seen as the next step in an effort to counter the economic rise of China and to promote factory growth in the United States. The officials cast it as a successor to the “Buy American” order that Mr. Biden signed last month.
The president’s order comes as a global shortage in semiconductors — a key component in cars and electronic devices — has forced several major American auto plants to close or scale back production and sent the administration scrambling to appeal to allies like Taiwan for emergency supplies.
The officials said the order would not offer a quick fix for that shortage. Instead, it would start an effort to insulate the American economy from future shortages of critical imported components.
Mr. Biden plans to order yearlong reviews of six sectors and a 100-day review of four classes of products where American manufacturers rely on imports: computer chips, high-capacity batteries, pharmaceuticals and their active ingredients, and critical minerals and strategic materials, like rare earths.
Subsequent actions to strengthen those supply chains will depend on the vulnerabilities that each review finds, the officials said.
The order is an early salvo in the administration’s economic battle with China. China’s dominance of global supply chains for critical products like medical masks and for raw materials has prompted deep concerns that Beijing’s authoritarian government could cut off the United States at a whim.
China has periodically moved to ban the export of rare earth materials that are crucial for manufacturing electronics, fighter jets and weaponry. Early in the coronavirus pandemic, Beijing halted exports of surgical masks and protective gear as it diverted supplies to its own local governments and hospitals.
Beijing has also sought to expand its foothold in certain emerging technologies by investing heavily in research and subsidizing new factories, raising concerns that China could dominate the supply of electric vehicles, advanced telecommunications gear and semiconductors in the same way it has cornered other global markets.
Key Data of the Day

The state of Virginia reported 172 coronavirus deaths on Tuesday, a 63 percent increase over 14 days, according to a New York Times database. But it also said that it knew of only two people who had died that day.
So what’s going on? Is Virginia experiencing a huge spike in deaths, or a remarkable lull?
The answer is neither. The wildly different figures are each accurate in their own way, but neither gives a complete picture — at least, not yet. Together, they illustrate an enduring problem with trying to track the pandemic in real time.
The daily death figures issued by most states, including Virginia, are a record-keeping measure: They count how many death certificates the state logged citing Covid-19, something that hardly ever happens the same day the deaths take place. Some certificates are filed fairly quickly by coroners’ offices, while others may take weeks to find their way into the state tallies.
On top of the daily arrivals, Virginia has lately been working through a big backlog of death reports left over from its surge of postholiday cases in December and the first half of January. This has led to somewhat staggering numbers of deaths being announced recently, including the 172 reported on Tuesday.
“The backlog of deaths reported comes from how soon those things are actually put onto a death certificate and then get to our office of vital records,” Dr. Norman Oliver, Virginia’s health commissioner, said on Wednesday during a news briefing.
Unlike many states, Virginia also publishes figures on deaths based on the dates they actually happened, and recommends using that data series “to observe the trends in Covid-19 deaths most effectively.” The trouble, though, is the time lag: The figures are never complete in real time because all the paperwork hasn’t come in yet.
So just as the 172 figure for Tuesday is really about the past, the two-death figure has not yet caught up with the present, and thus is almost sure to rise in the future.
Dr. Oliver said that once officials clear up the post-holiday backlog, he expects Virginia’s daily death reports to come down, to reflect the fall in new cases and hospitalizations in the state.
And by then, we will have a much better idea of how many people died on Tuesday.
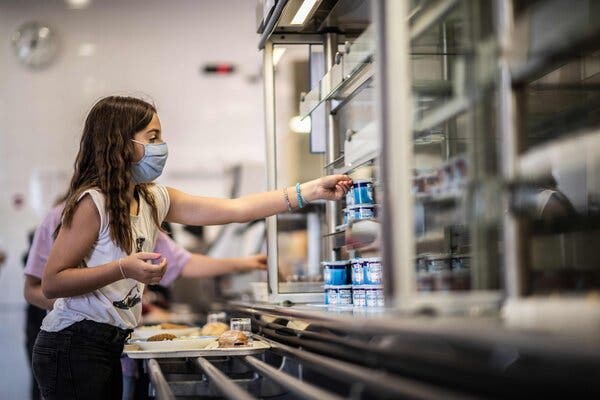

The closing of schools in nearly 200 countries as the coronavirus pandemic took hold last year abruptly deprived hundreds of millions of children of a school meal that, for many, was the only nutritious meal of the day. The United Nations World Food Program warned on Wednesday that with may schools still shut a year later, a decade’s worth of progress in improving children’s nutrition may be at risk of being erased.
“That one meal a day is often the reason hungry children go to school in the first place,” said David Beasley, the executive director of the World Food Program, as the organization released its annual report on school feeding. “It’s also a powerful incentive to make sure they’ll come back after lockdown ends.”
The organization called on governments around the world to maintain or even expand their school meal programs beyond pre-pandemic levels.
Studies have showed that food insecurity is associated with poor physical and mental health generally, and with reduced participation at school by children. When girls have access to school meals, they tend to stay in school longer, and rates of child marriage and teen pregnancy tend to decline.
Around 1.6 billion children were not able go to classrooms at the peak of the pandemic last year, and 370 million of them were deprived of a school meal as a result, putting them at risk of long-term health issues, according to the World Food Program.
Child food insecurity has become a concern in some developed countries during the pandemic. In Britain, activists like the soccer star Marcus Rashford have pushed the authorities to provide free meals to more children while schools remain closed.
But the risk may be greatest in low-income countries, where the number of children who were receiving school meals grew by 36 percent between 2013 and 2020, the World Food Program said.
“We need to get these programs running again — even better than before — to stop Covid destroying the futures of millions of the world’s most vulnerable children,” Mr. Beasley said.
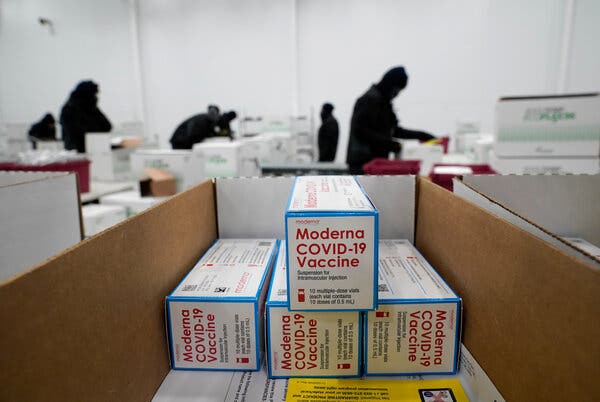

The drugmaker Moderna has created a new, experimental form of its coronavirus vaccine to combat a worrisome variant of the virus, and has also begun to increase its overall manufacturing capacity, the company announced on Wednesday.
The new version of the vaccine, directed against a variant first identified in South Africa and now found in the United States and dozens of other countries, has been sent to the National Institutes of Health for testing. Studies have suggested that vaccines may be less effective against this variant than against the form that emerged earlier in the pandemic.
But the new version is probably months away from public use. The company outlined several possible approaches for evaluating the experimental form. Initial test results may be available by summer, Dr. Tal Zaks, Moderna’s chief medical officer, said in an interview.
Moderna’s vaccine uses genetic material called mRNA, a technology that allows researchers to create and adapt vaccines much faster than traditional methods. The Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine is also based on mRNA, and Dr. Ugur Sahin, the chief executive of BioNTech, said last month that the company could produce a new version within about six weeks if necessary.
The Food and Drug Administration said on Monday that new versions of existing vaccines, adapted to target variants of the coronavirus, would not have to go through the same large trials in 30,000 or 40,000 patients as the first vaccines did.
Moderna said that its original vaccine still provides some protection against the variant, but that “out of an abundance of caution,” the company would pursue several new approaches.
One plan would use a shot of the new vaccine as a booster, after two doses of the original formulation.
Another strategy would be a booster shot combining the new vaccine and the original one.
A third approach, already underway, involves giving a third shot of just the original vaccine as a booster.
These booster shots would use a smaller dose of vaccine, 50 micrograms, instead of the 100 micrograms given in each of the shots now being administered in a two-dose series.
The company said it also planned to evaluate full, 100-microgram doses of the new vaccine and the combination shot as primary vaccinations, rather than merely boosters.
The company also said it was making new capital investments that it expected would enable it to manufacture 1.4 billion doses of coronavirus vaccine in 2022. That figure assumes that a dose is 100 micrograms, but if research finds that smaller amounts are effective, the number of doses would be even higher.
Moderna also said that its production plan for 2021 had increased, to 700 million doses from 600 million, and that it was trying to “potentially deliver up to 1 billion doses in fiscal year 2021.”
The company said it had already shipped 60 million doses globally, including about 55 million to the U.S. government, and expected to complete delivery of the first 100 million U.S. doses by the end of the first quarter of 2021, the second 100 million by the end of May and the third 100 million by the end of July.